Math 111 Notes: 9/20/2023
Section 1.7:
- >= over time became ≥ (greater than or equal to)
- <= over time became ≤ (less than or equal to)
- < (less than)
- > (greater than)
Read from left to right! For example: 3 < 4 or 4 > 3
5 ≤ 5…why is this true? Because of the equal to part =
3 ≥ 2 (this is true because >)
Example 1 in book: (-3,5] in interval notation, -3 is not included, 5 is included
Inequality form: -3 < x ≤ 5
x is present in (-3,5] …infinite number of values, so x stands for one of these values
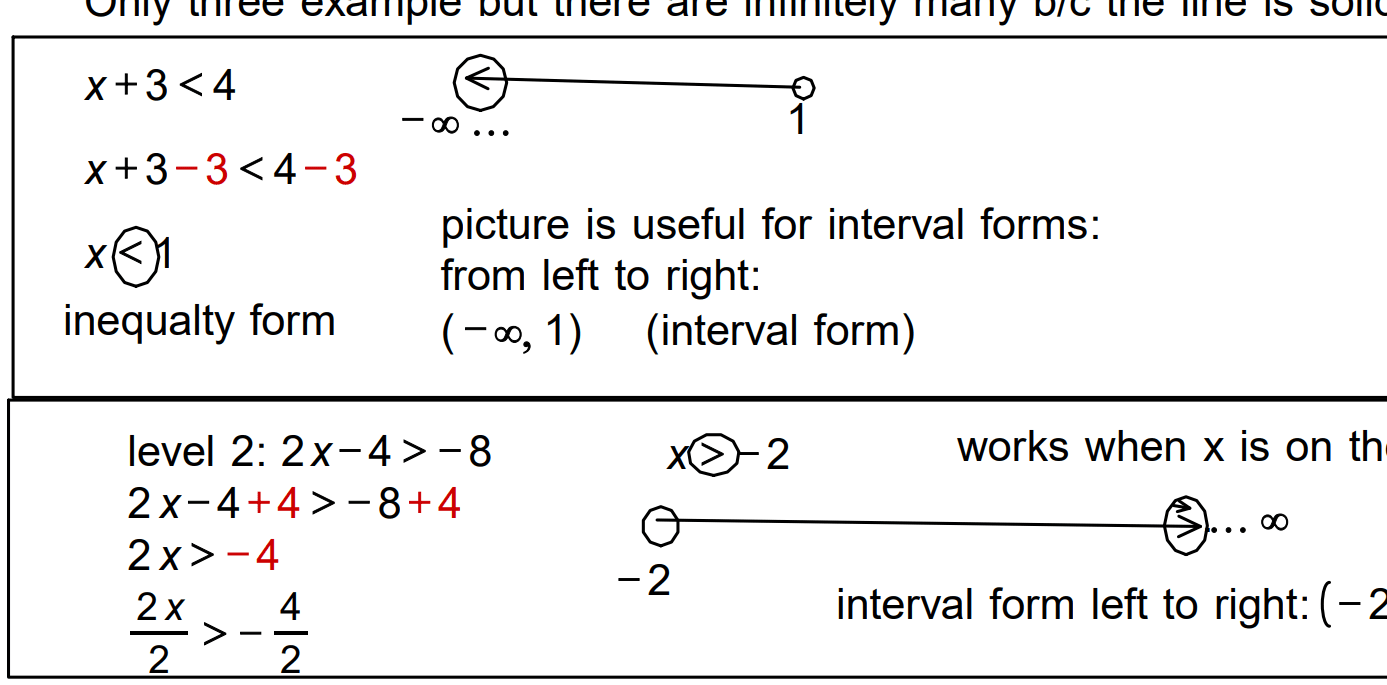
Example 2: 2x – 4 > -8
Solution: x > -2
Example 3 in book: 1 – 3/2x ≥ x – 4
Solution: x ≤ 2
Example 4 in book: -3 ≤ 6x – 1 < 3
Solution: -1/3 ≤ x < 2/3
Example 5 in book: x = -2 because -2 > 1 → 2 > 1 is true!
Example 6: Two phone plans…
Plan A Cost: 49.99 + 0.4m
Plan B Cost: 45.99 + 0.45m
How many additional minutes must you use in one month for plan B to cost more than plan A?
Solution: m > 80 minutes! Plan B costs more if you use more than 80 additional minutes in one month!
Example 7: You go to a store to buy chocolates that cost $9.89 per pound.
The scale used in the store has a state seal of approval that indicates the scale is accurate to within half an ounce. (or 1/32 of a pound)
According to the scale, your purchase weighs one-half pound and costs 4.95$. How much might you have been undercharged or overcharged as a result of an inaccuracy in the scale?
Solution: You might have been undercharged by $0.30 or overcharged by $0.30.
Understandin Creating Solving And Applying Linear Inequalities