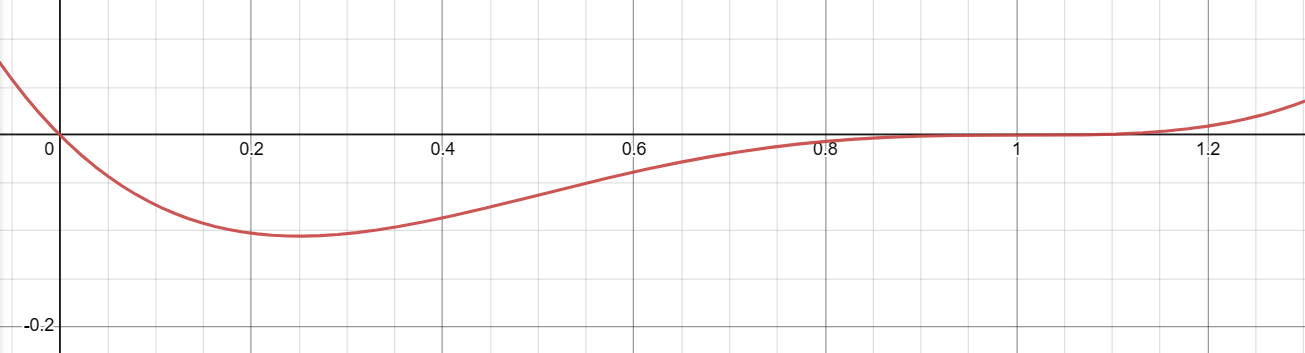
Decoding the Graph of f(x) = x(x-1)³: A Comprehensive Visual Guide
Key Features of the Graph
- Roots: The function has roots at x=0 and x=1.
- Multiplicities: The root at x=0 has a multiplicity of 1, meaning the graph crosses the x-axis linearly at this point. The root at x=1 has a multiplicity of 3, causing the graph to “bounce” off the x-axis at this point.
- End Behavior: As x approaches negative infinity or positive infinity, the function also approaches negative or positive infinity, respectively.
- Turning Points: The graph has turning points near x=0 and x=1, corresponding to the roots and their multiplicities.
Why the Graph is Flatter at x=1
The graph appears flatter at x=1 due to the higher multiplicity of the root at this point. A higher multiplicity often results in the graph “slowing down” as it approaches the root, making it appear flatter.
Visual Characteristics
The graph starts from the second quadrant (top-left), crosses the x-axis at x=0, dips back into the third quadrant, and then rises to “bounce” off the x-axis at x=1 before heading towards positive infinity.
The “bounce” at x=1 is more pronounced and flatter than the linear crossing at x=0 due to the higher multiplicity of the root at x=1.
Interpreting the Graph
The graph’s behavior is heavily influenced by the multiplicities of its roots. The linear crossing at x=0 and the “bounce” at x=1 are direct manifestations of these multiplicities.
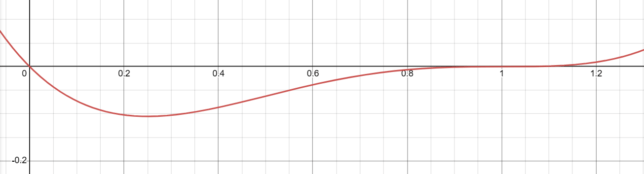
Behavior of f(x) = x(x-1)³ Near x=0
Multiplicity at x=0
The function has a root at x=0 with a multiplicity of 1. This means the function crosses the x-axis at x=0 in a linear manner.
Table of Calculations Close to x=0
| x Value Near 0 | Value of (x-1)³ | Value of f(x) = x(x-1)³ |
|---|---|---|
| -0.1 | -1.0001 | 0.10001 |
| -0.01 | -1.000001 | 0.00001000001 |
| 0 | -1 | 0 |
| 0.01 | -0.999999 | -0.00000999999 |
| 0.1 | -0.9999 | -0.09999 |
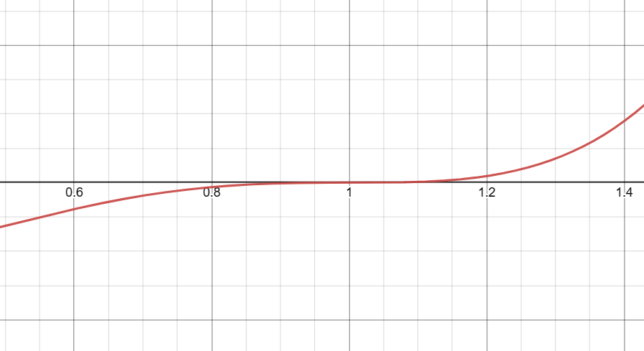
Behavior of f(x) = x(x-1)³ Near x=1
Multiplicity at x=1
The function has a root at x=1 with a multiplicity of 3. This means the function “bounces” off the x-axis at x=1, rather than crossing it.
Table of Calculations Close to x=1
| x Value Near 1 | Value of (x-1)³ | Value of f(x) = x(x-1)³ |
|---|---|---|
| 0.9 | -0.001 | -0.0009 |
| 0.99 | -0.000001 | -0.00000099 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1.01 | 0.000001 | 0.00000101 |
| 1.1 | 0.001 | 0.0011 |