3-Vector Scalar Projection Calculator
Vector A
Vector B
Understanding Scalar Projection
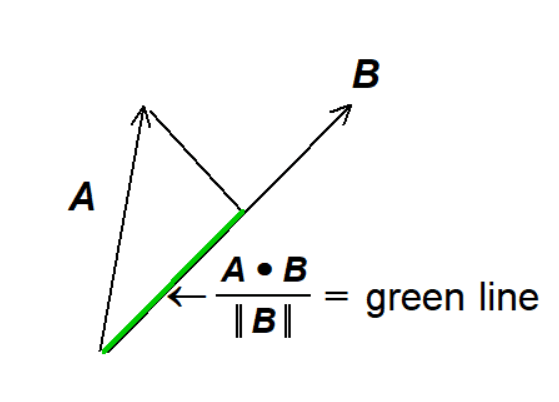
The scalar projection of a vector \( \textbf{A} \) onto another vector \( \textbf{B} \) is a measure of how much \( \textbf{A} \) “projects” onto \( \textbf{B} \). It is a scalar value that can be positive, negative, or zero.
The formula for calculating the scalar projection of \( \textbf{A} \) onto \( \textbf{B} \) is:
\[ \text{Scalar Projection} = \frac{\textbf{A} \cdot \textbf{B}}{||\textbf{B}||} \]
Where:
- \( \textbf{A} \cdot \textbf{B} \) is the dot product of \( \textbf{A} \) and \( \textbf{B} \).
- \( ||\textbf{B}|| \) is the magnitude of \( \textbf{B} \).
This calculator performs these calculations step-by-step, providing you with the scalar projection value.
Acceptable Input Formats
This calculator accepts decimal numbers in the following formats:
- Whole Numbers: e.g., 1, 2, 3
- Decimal Numbers: e.g., 1.2, 2.75, 3.333
- Negative Numbers: e.g., -1, -1.5, -2.75
- Zero: 0
Please note that fractions (e.g., 1/2, 2/3) are not supported and should be converted to decimal form before entering them. The calculator uses JavaScript’s parseFloat() function, which only understands decimal notation.