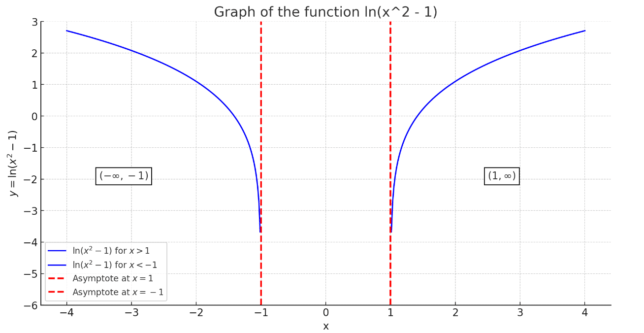
Determining the Domain of ln(x² – 1)
To find the domain of ln(x² – 1), we must find the set of x values for which x² – 1 is positive, since the logarithm function ln(x) is defined only for x > 0.
First, we factor the expression x² – 1:
- x² – 1 = (x – 1)(x + 1)
The zeros of the expression (x – 1)(x + 1) are x = 1 and x = -1. We analyze the intervals determined by these zeros to find where (x – 1)(x + 1) > 0.
For x < -1, say x = -2:
- ln((-2)² – 1) = ln(4 – 1) = ln(3), which is defined.
For -1 < x < 1, say x = 0:
- ln((0)² – 1) = ln(-1), which is not defined for real numbers.
For x > 1, say x = 2:
- ln((2)² – 1) = ln(4 – 1) = ln(3), which is defined.
Therefore, the domain of ln(x² – 1) is x < -1 or x > 1, which in interval notation is (-∞, -1) ∪ (1, ∞).