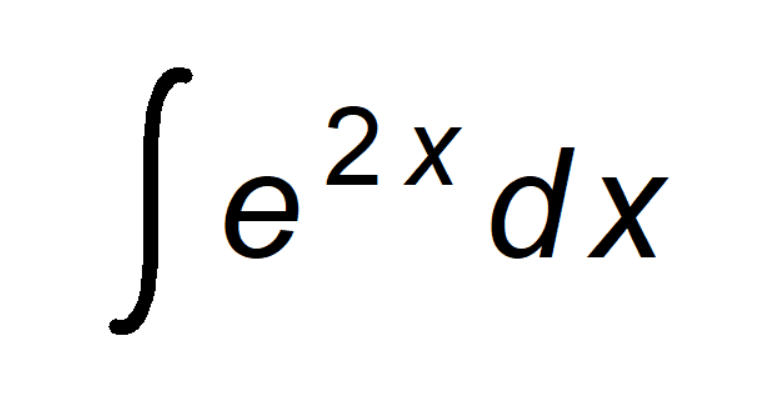1. Start with the integral you want to solve:
∫ e²ˣ dx
This represents the area under the curve of e²ˣ.
2. Make a substitution for the exponent, letting u = 2x:
∫ eᵘ · (du/2)
By letting u = 2x, we simplify the expression, and (du/2) accounts for the chain rule.
3. Integrate eᵘ with respect to u:
(1/2) ∫ eᵘ du = (1/2) eᵘ + C
The integral of eᵘ is simply eᵘ, and we multiply by (1/2) to account for the earlier substitution.
4. Substitute back for u:
(1/2) e²ˣ + C
Replacing u with 2x gives the final result.
So the integral of e²ˣ is (1/2) e²ˣ + C, where C is the constant of integration.