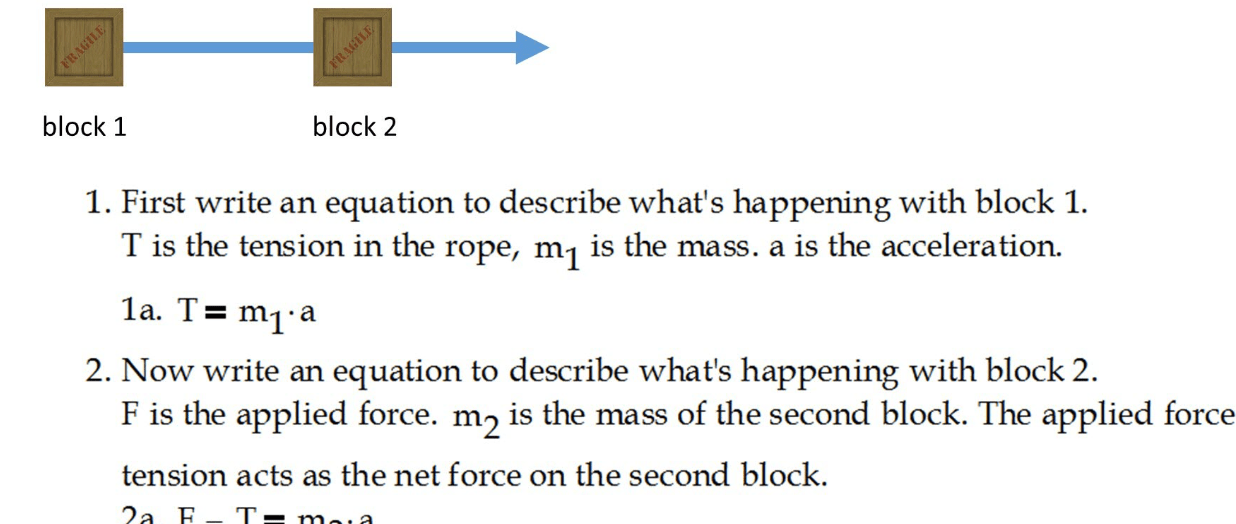
Finding Tension and Acceleration in a Two-Block System with a Frictionless Pulley
Keyphrase: Two-Block System with a Frictionless Pulley
This section provides a detailed analysis of a two-block system connected by a rope over a frictionless pulley. We will find the tension in the rope and the acceleration of the system.
System Description:
- Block A has mass \( m_A \) and is placed on a horizontal surface.
- Block B has mass \( m_B \) and is suspended vertically.
- The blocks are connected by a rope over a frictionless pulley.
Constructing the Equations of Motion for the Two-Block System with a Frictionless Pulley:
For Block A (horizontal motion):
- The tension \( T \) in the rope is pulling Block A to the right.
- Using Newton’s second law, the equation for Block A is: \( m_A \cdot a = T \).
- Visualize this as a tug-of-war between the tension pulling Block A and the inertia of Block A resisting the motion.
For Block B (vertical motion):
- The gravitational force on Block B is \( m_B \cdot g \), pulling it downward.
- The tension \( T \) in the rope is pulling Block B upward.
- Using Newton’s second law, the equation for Block B is: \( m_B \cdot a = m_B \cdot g – T \).
- Visualize this as a balance between the gravitational pull on Block B and the tension in the rope pulling it upward.
Solving for Tension and Acceleration:
- Combine the Equations: Combine the equations for Block A and Block B to form a system of equations.
- Solve for Acceleration and Tension: Solve the system of equations to find the values of \( a \) and \( T \).
Conclusion:
This analysis of the Two-Block System with a Frictionless Pulley breaks down every aspect of the system, including the tension and acceleration. Understanding these properties is essential for various applications in physics and engineering.
Sketching the Two-Block System with a Frictionless Pulley
Keyphrase: Sketching Two-Block System with Frictionless Pulley
This section provides a step-by-step guide to sketching a two-block system connected by a rope over a frictionless pulley. The sketch will include Block A on a horizontal surface, Block B suspended vertically, and a frictionless pulley at the edge connecting them.
Steps to Sketch the System:
- Draw the Horizontal Surface: Begin by drawing a horizontal line to represent the surface on which Block A is placed.
- Sketch Block A: Draw a rectangle above the horizontal line near the left end to represent Block A. Label it “A” and include its mass \( m_A \).
- Draw the Frictionless Pulley at the Edge: Sketch a small circle at the right end of the horizontal line to represent the frictionless pulley at the edge of the surface.
- Sketch Block B: Draw another rectangle below the pulley to represent Block B. Label it “B” and include its mass \( m_B \).
- Connect the Blocks with a Rope: Draw a line connecting Block A to the pulley and another line connecting the pulley to Block B. This line represents the rope.
- Add Arrows for Forces: Draw an arrow pointing right from Block A to represent the tension pulling it. Draw an arrow pointing down from Block B to represent the gravitational force, and an arrow pointing up to represent the tension pulling it upward.
- Label the Tension and Acceleration: Include labels for the tension \( T \) and the acceleration \( a \) of the system.
Conclusion:
This step-by-step guide provides a clear and concise method for sketching the Two-Block System with a Frictionless Pulley at the edge of the surface. Understanding how to visualize this system is essential for solving problems related to tension, acceleration, and motion in physics and engineering.